Tips for Preventing Catheter-Associated UTIs
Posted by Jeanne Lowry on Oct 27th 2023
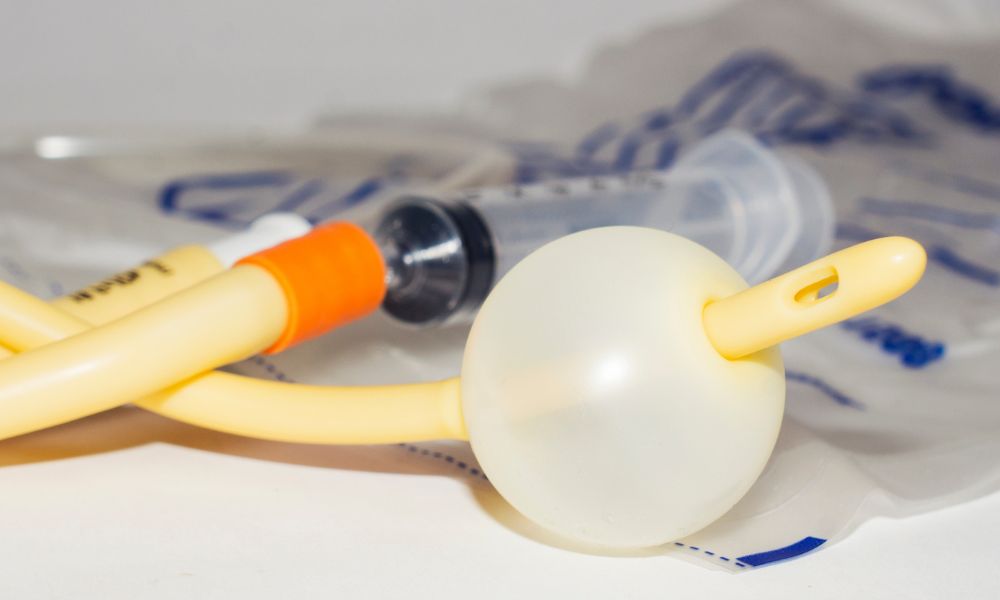
Catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) can be a significant concern for many individuals who rely on urinary catheters for urinary problems. Protecting against these infections should be a top priority for those who use catheters regularly. With the right knowledge and preventative measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of getting one. That’s why we’re here to go over what a catheter-associated UTI is and how to prevent it from happening in the first place.
Understanding Catheter-Associated UTIs
A catheter-associated UTI refers to a urinary tract infection that occurs due to the presence of a catheter. This type of UTI is typically the result of bacteria entering the urinary tract via the catheter, where they can multiply and cause infection. Given the potential complications that can arise from a UTI, you want to be informed and proactive about preventing and addressing CAUTIs.
Recognizing the Signs of a UTI
Of course, detection is much more difficult if you don’t know what to look for. Since early detection is crucial when addressing a CAUTI, the quicker you can identify one, the better your chances of preventing further complications. Some common signs of a UTI include:
- Cloudy, bloody, or foul-smelling urine
- Increased urgency or frequency of urination
- Pain or discomfort in the abdomen, lower back, or pelvic area
- Fever, chills, or general soreness
If you suspect that you may be experiencing a CAUTI, consult with a health-care professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Once you know what you’re dealing with, it’ll be easier to treat it.
The Dangers of Untreated CAUTIs
Ignoring these symptoms will only make things worse. If left untreated, catheter-associated UTIs can lead to serious health issues. These can include kidney infection (pyelonephritis)—which can result in kidney damage—and bloodstream infection (sepsis)—which can be potentially life-threatening.
Even if the end result isn’t one of these two, a CAUTI can lead to prolonged hospital stays and increased health-care costs, neither of which are desirable outcomes. That’s why you must take the necessary precautions and seek treatment if you suspect that you may have a CAUTI.
CAUTI Prevention Tips
Since you’ll want to do everything you can to avoid these complications, you’ll likely want to know what you can do to make sure they never happen in the first place. Here’s a list of tips that’ll help you prevent catheter-associated UTIs from ever occurring.
Prioritize Hygiene
Proper hygiene is an important factor in reducing the risk of catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Wash the area around the catheter insertion site daily using a gentle cleanser, as this minimizes bacterial growth and potential infection.
Additionally, thorough handwashing before and after handling the catheter is crucial in preventing the spread of germs to the catheter site. To further enhance hygiene practices, consider using disposable gloves when changing the catheter or in situations where there may be an increased risk of infection. While this isn’t necessary, it adds an additional layer of protection for those times when handwashing isn’t enough.
Furthermore, opting for a sterile catheter can provide an added layer of protection.
Use the Right Catheter and Technique
On top of hygiene, the type of catheter and insertion technique you use can significantly impact the risk of CAUTIs. Opt for a catheter that suits your specific needs. For example, if you’re a man who has trouble making it to the bathroom regularly, you’ll want to use a male Foley catheter over an intermittent one. Of course, there are also female versions if you’re a woman with the same issue. Either way, if you’re unsure about the most appropriate catheter for you, consult a health-care professional for guidance.
When inserting your new catheter, make sure to follow sterile techniques and guidelines provided by the catheter manufacturer. If there aren’t detailed instructions, your doctor can assist you. Generally, proper lubrication and care can go a long way in minimizing discomfort and potential injury to the urinary tract, thereby reducing the risk of infection.
Check the Catheter’s Integrity
For those who have catheters that they use for long periods of time, regular inspection of their integrity is another essential part of mitigating the risk of catheter-associated urinary tract infections. The catheter should be free of kinks, blockages, or any signs of damage. Faulty catheters can lead to incomplete emptying of the bladder, which can promote bacterial growth and hence increase the risk of CAUTIs.
Also, check the catheter tubing for any signs of sediment or blockages, as this can disrupt the normal flow of urine and create a conducive environment for bacteria to flourish. In the event of any abnormalities, you must change the catheter promptly. Doing so will help you avoid the possibility of a CAUTI.
Regularly Empty and Clean the Drainage Bag
When you have a drainage bag that collects the urine from your catheter, you must empty it consistently. Overfilling could cause a backflow of urine and potentially introduce bacteria into your urinary system. As a general rule, consider emptying the bag when it’s half-full.
Also, you must clean the drainage bag periodically. Following the cleaning instructions provided by the manufacturer or your health-care professional will reduce the risk of bacteria reentering your system.
Keep the Collection Bag Below the Bladder Level
Even if you get better at emptying your collection bag regularly, it’s still possible to have urine reenter your urinary tract if you’re not careful. This happens when you store your collection bag at a higher elevation than your bladder. This is especially important to pay attention to when you’re lying down.
Whether resting or sleeping, you need to make sure your collection bag sits at a lower elevation. This is the best way to ensure that there’s no backflow.
Remember When To Change Your Catheter
Finally, make sure to change your catheter according to the recommended guidelines provided by either the manufacturer or your health-care professional. These guidelines are in place to minimize the risk of infection, so following them diligently is crucial. Failing to keep up with this schedule will make a CAUTI much more likely.
One Final Note: CAUTIs Are Always a Possibility
Even if you follow all these tips to the letter, a CAUTI is still possible. Infections are an issue that can happen to anyone. If you ever suspect that you have developed a CAUTI or experience one of the previously mentioned symptoms that could indicate an infection, seek medical attention immediately. The sooner you discover the issue, the easier it’ll be to prevent more severe complications and stay on the path to optimal health.